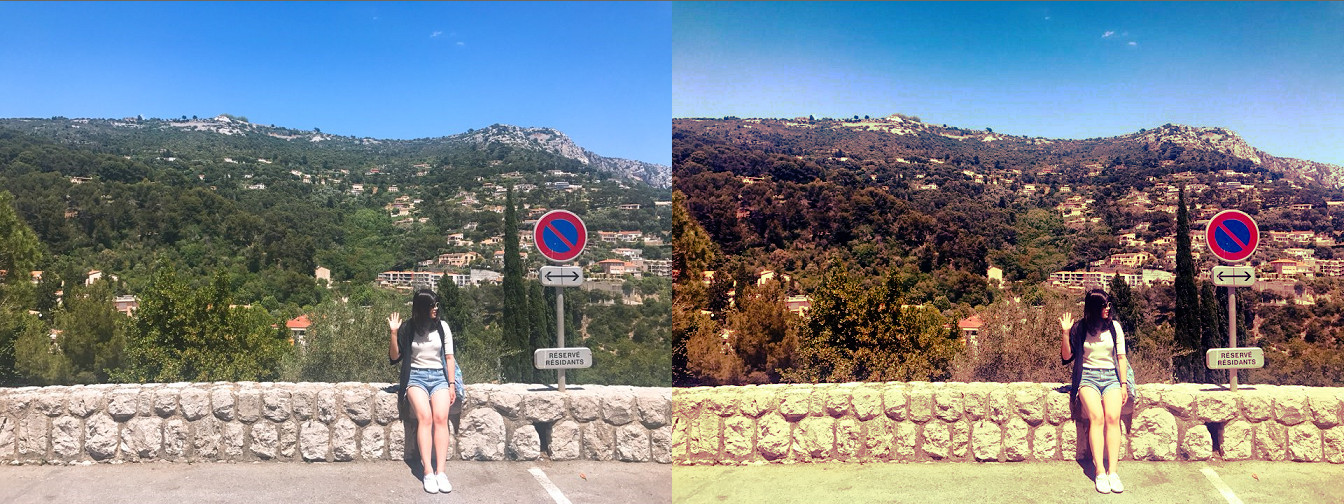
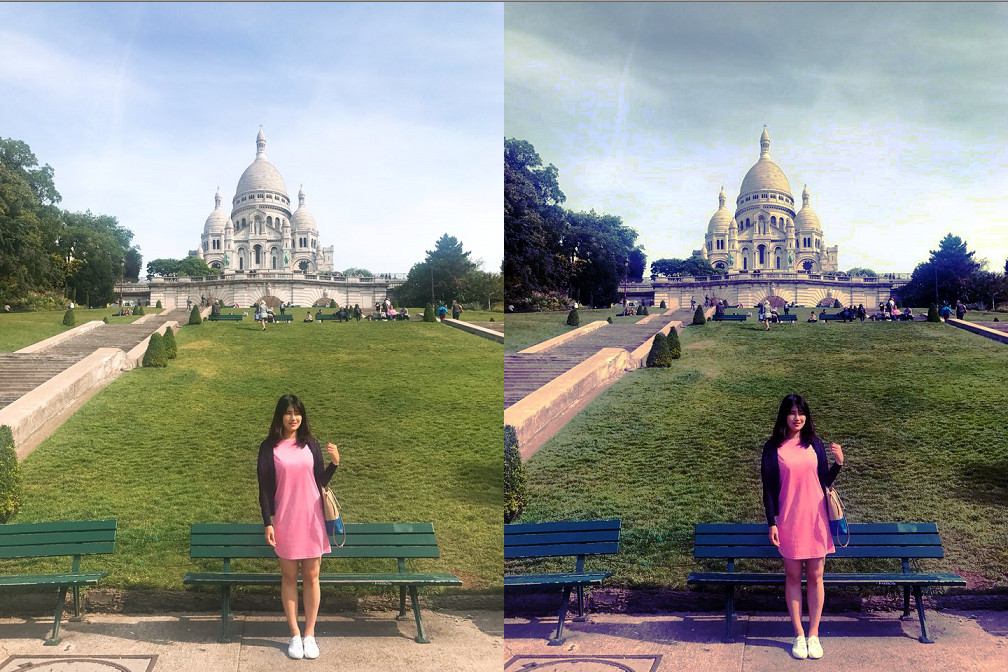
Histogram Equaliztion(히스토그램 평활화)을 알아보자
2018, Jun 27
히스토그램 평활화란 명암 값의 분포가 한쪽으로 치우친 영상이 있을 때, 명암값을 고르게 분포시켜주기 위한 처리 방법을 말한다. 예를 들어, 어두운영역에서 세밀한 영상이 있을 때 히스토그램평활화를 이용하면 보다 밝은 영상으로 세밀한 부분을 볼 수 있을 것이다.
히스토그램 평활화는 다음의 단계를 거친다.
- 그림의 히스토그램을 구한다.
- 히스토그램의 누적 히스토그램의 구하고 정규화 한다.
- 이미지에 정규화된 누적 히스토그램의 값을 적용한다.
위 기능을 구현할 수 있는 함수를 정의하자. 헤더파일 선언부는 생략하겠다.
ImageProc.cpp
void ImageProc::CreateCumulativeHistogramSingleChannel(unsigned char* image_input,
unsigned char* image_output, const int width, const int height)
{
// 1. 히스토그램을 만든다.
float histogram[256] = { 0.f };
for (int i = 0; i < width*height; i++)
histogram[image_input[i]]++;
// 2. 누적히스토그램을 만든다.
float cumulative_histogram[256] = { 0.f };
float sum = 0.f;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
sum += histogram[i];
cumulative_histogram[i] = sum;
}
// 누적히스토그램을 정규화한다.
// 정규화 = (값 / 최대값(이미지 사이즈)) * 픽셀최대값(255)
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
cumulative_histogram[i] = (cumulative_histogram[i] / (width * height)) * 255 + 0.5f;
// 3. 이미지에 적용한다.
for (int i = 0; i < width*height; i++)
image_output[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>(cumulative_histogram[image_input[i]]);
}위는 단일 채널에서만 가능한 함수이므로, 칼라이미지에서 평활화 가능한 함수를 정의한다.
ImageProc.cpp
void ImageProc::CreateHistogramEqualization(unsigned char* image_input,
unsigned char* image_output, const int width, const int height)
{
unsigned char* img_R = new unsigned char[width*height];
unsigned char* img_G = new unsigned char[width*height];
unsigned char* img_B = new unsigned char[width*height];
SplitChannels_ColorToRGB(img_R, img_G, img_B, image_input, width, height);
unsigned char* equal_R = new unsigned char[width*height];
unsigned char* equal_G = new unsigned char[width*height];
unsigned char* equal_B = new unsigned char[width*height];
//SplitChannels_ColorToRGB(equal_R, equal_G, equal_B, image_output, width, height);
CreateCumulativeHistogramSingleChannel(img_R, equal_R, width, height);
CreateCumulativeHistogramSingleChannel(img_G, equal_G, width, height);
CreateCumulativeHistogramSingleChannel(img_B, equal_B, width, height);
MergeChannels_RGBToColor(equal_R, equal_G, equal_B, image_output, width, height);
delete[] img_R;
delete[] img_G;
delete[] img_B;
delete[] equal_R;
delete[] equal_G;
delete[] equal_B;
}
이벤트 처리기를 정의하자. 그전에 SetDrawImage 를 아래와 같이 수정한다. 수정하는 이유는 기존에 흑백이미지만 오른쪽 화면에 나올 수 있는데, 이제 칼라이미지도 나올 수 있게 하기 위해서 이다.
ImageProcessingView.cpp
void CImageProcessingView::SetDrawImage(unsigned char* image, unsigned char* image_gray,
const int width, const int height, const int byte)
{
m_ImgWidth = width * 2;
m_ImgHeight = height;
if (m_Image)
delete[] m_Image;
// 화면을 두 배로 써야 하기 때문에 *2를 해준다.
m_Image = new unsigned char[width * 2 * height * 4];
for (int i = 0; i<width; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++)
{
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i) * 4 + 0] = image[(width*j + i) * 4 + 0];
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i) * 4 + 1] = image[(width*j + i) * 4 + 1];
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i) * 4 + 2] = image[(width*j + i) * 4 + 2];
}
}
// color image 다음에 gray image 가 오면 흑백이미지 처리를 해준다.
if (byte == 1)
{
for (int i = 0; i<width; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++)
{
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i + width) * 4 + 0] = image_gray[(width*j + i)];
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i + width) * 4 + 1] = image_gray[(width*j + i)];
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i + width) * 4 + 2] = image_gray[(width*j + i)];
}
}
}
// color image 가 다음에 나오면 color image 처리를 해준다.
else
{
for (int i = 0; i<width; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++)
{
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i + width) * 4 + 0] = image_gray[(width*j + i)*byte + 0];
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i + width) * 4 + 1] = image_gray[(width*j + i)*byte + 1];
m_Image[(m_ImgWidth*j + i + width) * 4 + 2] = image_gray[(width*j + i)*byte + 2];
}
}
}
}
이벤트 처리기를 단다.
ImageProcessingDoc.cpp
void CImageProcessingDoc::OnHistogramHistogramequalization()
{
// TODO: 여기에 명령 처리기 코드를 추가합니다.
histogram_equalization_image =
new unsigned char[m_Images[cur_index].width * m_Images[cur_index].height *4];
( 클래스 변수로 설정하고 소멸자에서 해당 버퍼를 delete 하는 기능을 추가한다. )
memset(histogram_equalization_image, 0, sizeof(unsigned char)
*m_Images[cur_index].width * m_Images[cur_index].height * 4);
ImageProc::CreateHistogramEqualization(m_Images[cur_index].image_color,
histogram_equalization_image, m_Images[cur_index].width, m_Images[cur_index].height);
CImageProcessingView* pView = (CImageProcessingView*)((CMainFrame*)(AfxGetApp()->m_pMainWnd))->GetActiveView();
pView->SetDrawImage(m_Images[cur_index].image_color, histogram_equalization_image,
m_Images[cur_index].width, m_Images[cur_index].height, 4);
pView->OnInitialUpdate();
}
실행하면 다음과 같이 이미지의 명암이 고루 분포된다.